Advanced charts
Advanced charts are a powerful way to display complex data sets. While less intuitive than basic charts, the visualizations should still tell a story the user can understand.
Note: The advanced charts are not included in the Carbon Charts repostitory yet. To see our roadmap, make feature requests, or contribute, please go to carbon-charts GitHub repository.
Alluvial diagram
Alluvial diagrams are a type of flow diagram originally developed to represent changes in network structure over time.
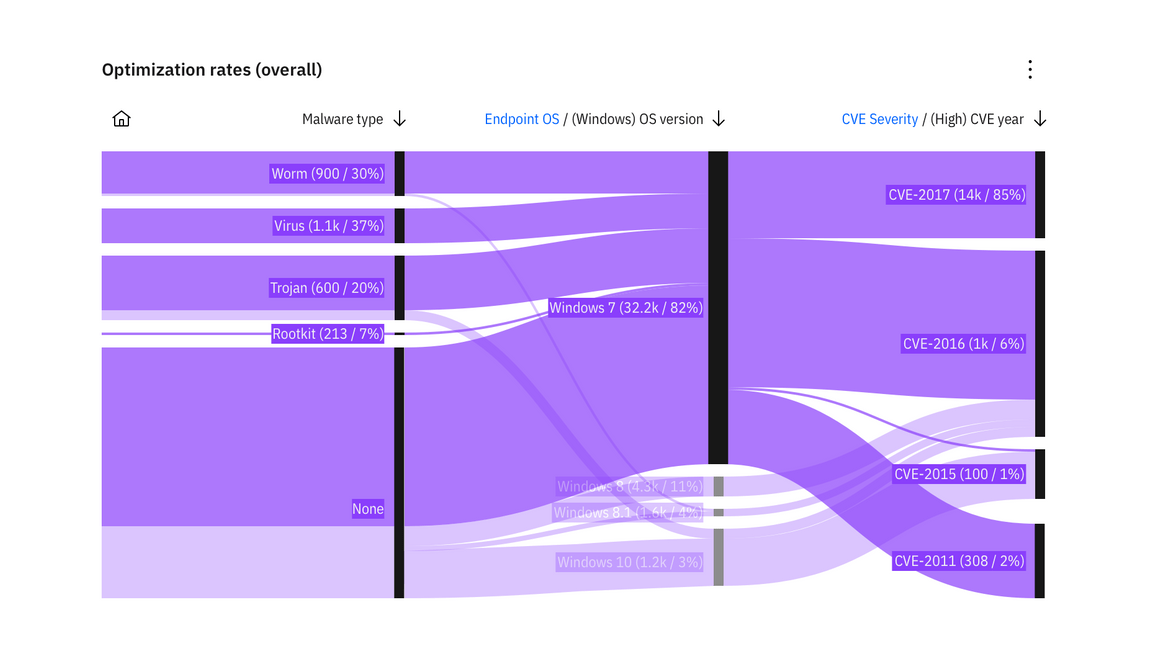
Example of an alluvial diagram
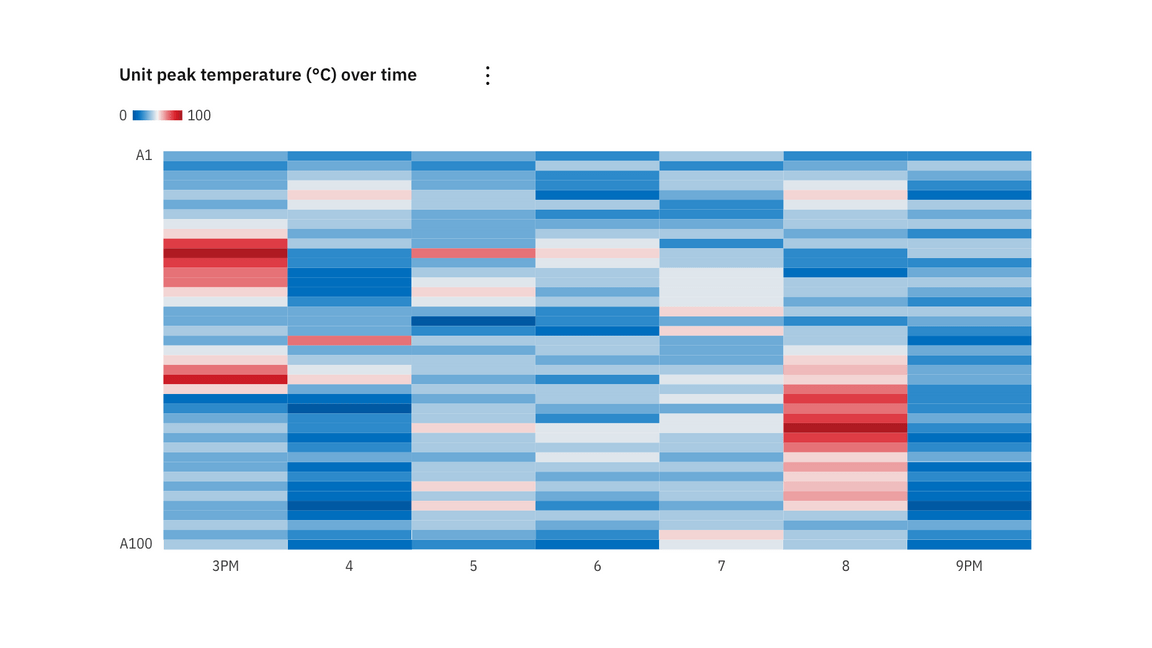
Heatmap
A heat map is a graphical representation of data where the individual values contained in a matrix are represented as colors.
Tree diagram
A Tree Diagram is a way of visually representing hierarchy in a tree-like structure.
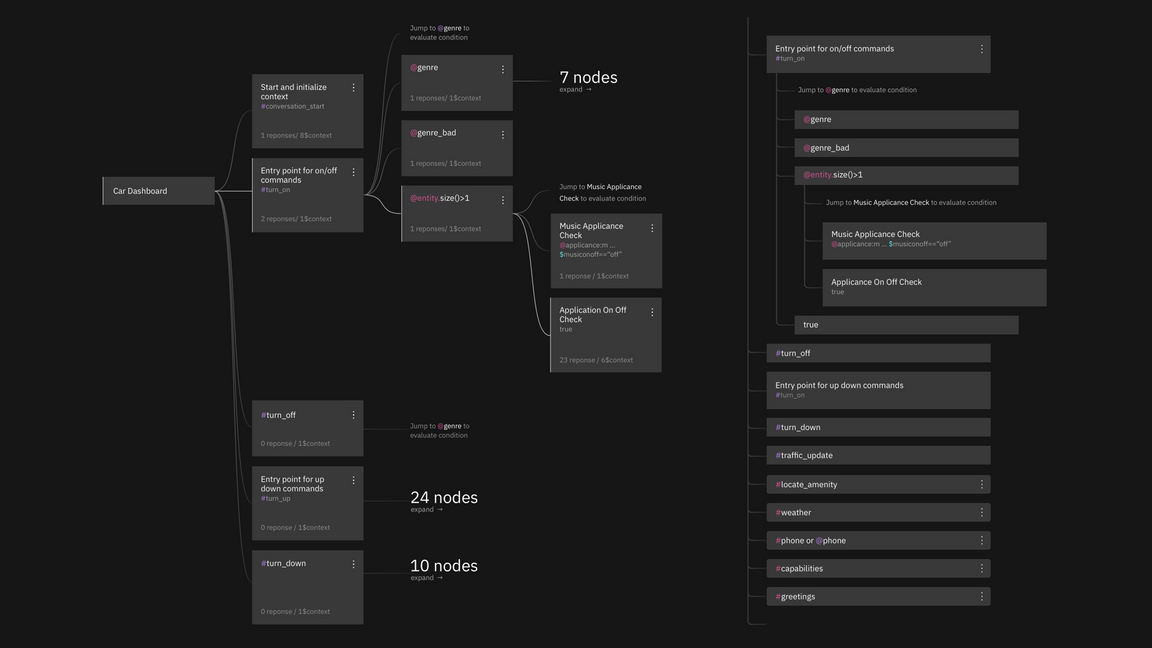
Tree diagram, node view vs list view.
Geography with overlays
Choropleth map
A map that uses differences in shading, coloring, or the placing of symbols within predefined areas to indicate the average values of a property or quantity in those areas.
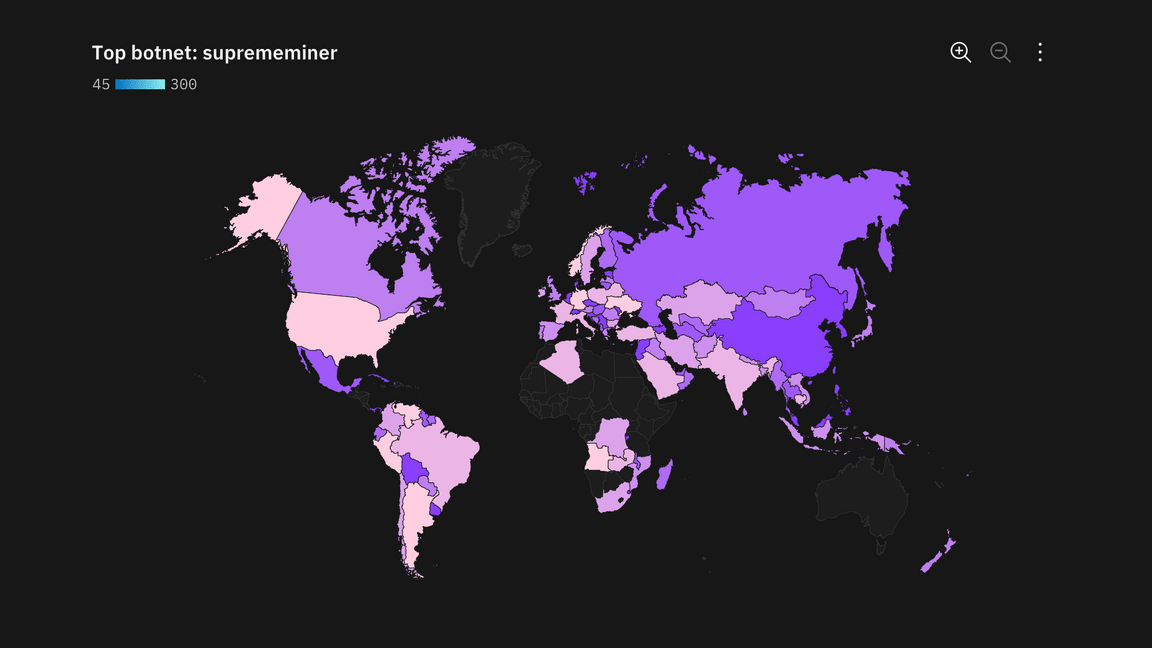
Example of a choropleth map
Proportional symbol
Symobls driven by data are overlayed on geographical region. A common symbol used is bubble with the area of the circle proportional to its value in the dataset.
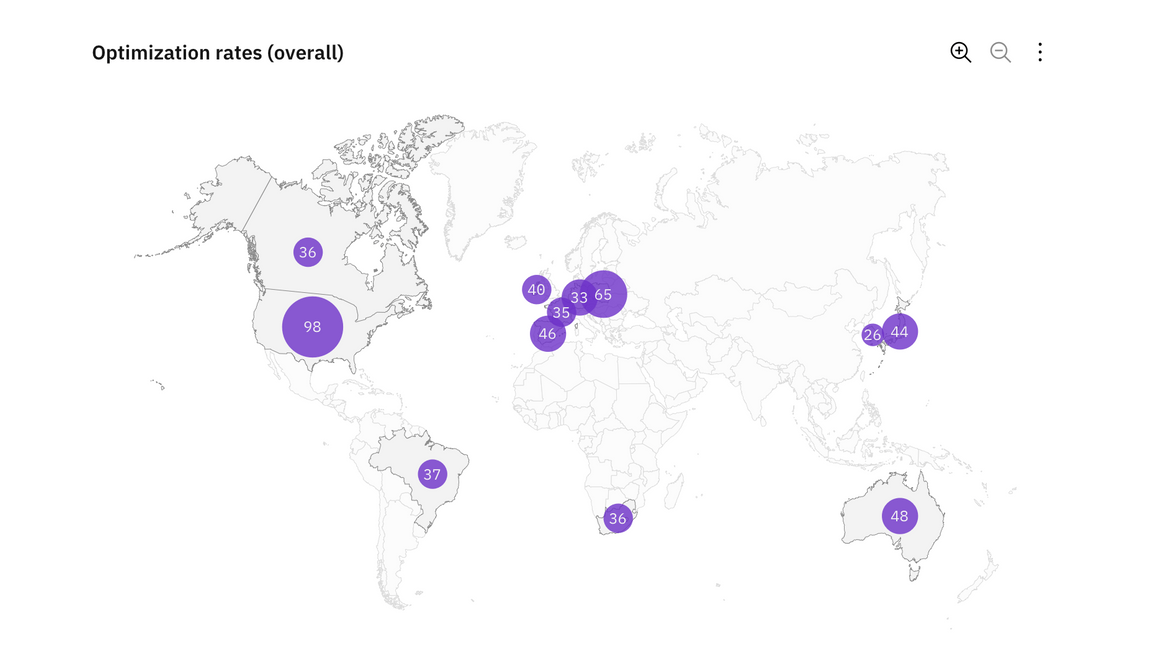
Example of a proportional symbol
Connecting lines
Connection Maps are drawn by connecting points placed on a map by straight or curved lines.
While Connection Maps are great for showing connections and relationships geographically, they can also be used to display map routes through a single chain of links. Connection Maps can also be useful in revealing spatial patterns through the distribution of connections or by how concentrated connections are on a map.
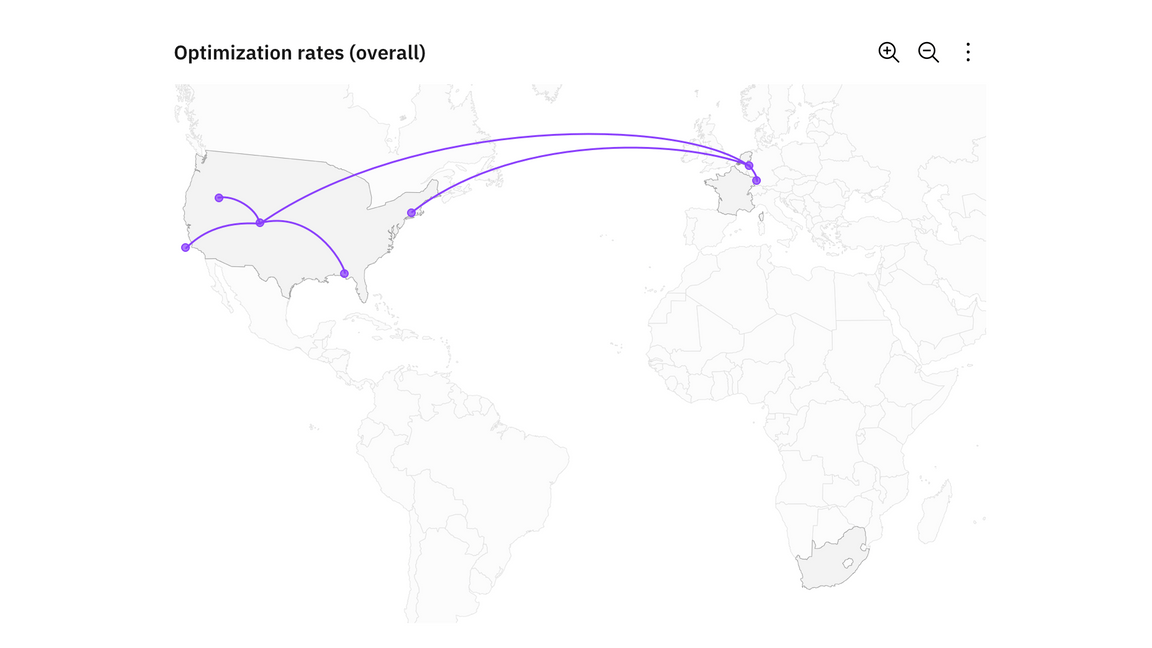
Example of a map with connecting lines